Atherosclerosis Is Characterized by the Deposition of Lipids in the:
Atherosclerosis is a complex inflammatory disease characterized by lipid accumulation within the artery walls. Lipid homeostasis especially cholesterol homeostasis plays a crucial role during the.

Atherosclerosis Pathology Britannica
Eventually these lesions cause luminal stenosis and potentially culminate in thrombotic occlusion andor embolism.

. Plaque rupture and the consequent thrombosis may. Begins with arterial endothelial injury - atheroma lipid cholesterol core develops - arterial blood flow descreases. The formation of plaques involves the deposition of small cholesterol crystals in the intima and its underlying smooth muscle.
Atherosclerosis is a progressive disease characterized by the accumulation of lipids and fibrous elements in the large arteries. Type of arteriosclerosis characterized by thickening and lipid deposition in the tunica intima of arteries inflammatory disease overview of stages of development of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is characterized by vascular obstruction from the deposits of plaque resulting in reduced blood flow.
The core region of atherosclerotic plaques is characterized by profuse lipid deposition and disappearance of cells and fibrous tissue elements. Lipid homeostasis especially cholesterol homeostasis plays a crucial role during the formation of foam cells. Lipid homeostasis especially cholesterol homeostasis plays a crucial role during the formation of foam cells.
The formation of macrophage-derived foam cells in a plaque is a hallmark of the development of atherosclerosis. Up to 10 cash back Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by the deposition of excess lipids in the arterial intima. Form of arteriosclerosis characterized by the deposition of atheromatous plaques containing cholesterol and lipids on the innermost layer of the walls of large and mediumsized arteriesThe condition in which an artery wall thickens as the result of a build-up of fatty materials such as cholesterolHardening of the arteriesA form of arteriosclerosis in which fatty deposits.
The early lesions of atherosclerosis consist of subendothelial accumulations of cholesterol-engorged macrophages called foam cells. Atherosclerosis is primarily an arterial disorder classically characterized by lipid deposition in the vessel intima and associated with inflammation scarring and calcification. Atherosclerosis is associated with inflammatory processes in the endothelial cells of the vessel wall associated with retained low-density lipoprotein LDL particles.
25 26 This retention may be a cause an effect or both of the underlying inflammatory process. Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by the deposition of excess lipids in the arterial intima. The formation of macrophage-derived foam cells in a plaque is a hallmark of the development of atherosclerosis.
The anatomy of a normal artery is shown in Fig. The formation of macrophage-derived foam cells in a plaque is a hallmark of the development of atherosclerosis. It produces the narrowing of arteries due to the development of intimal plaques.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by the deposition of excess lipids in the arterial intima. Atherosclerosis is the leading cause of death in North America and within the next two decades will be the leading cause worldwide.

Accumulation Of Plasma Derived Lipids In The Lipid Core And Necrotic Core Of Human Atheroma Imaging Mass Spectrometry And Histopathological Analyses Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis And Vascular Biology

The Role Of Lipids And Lipoproteins In Atherosclerosis Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf
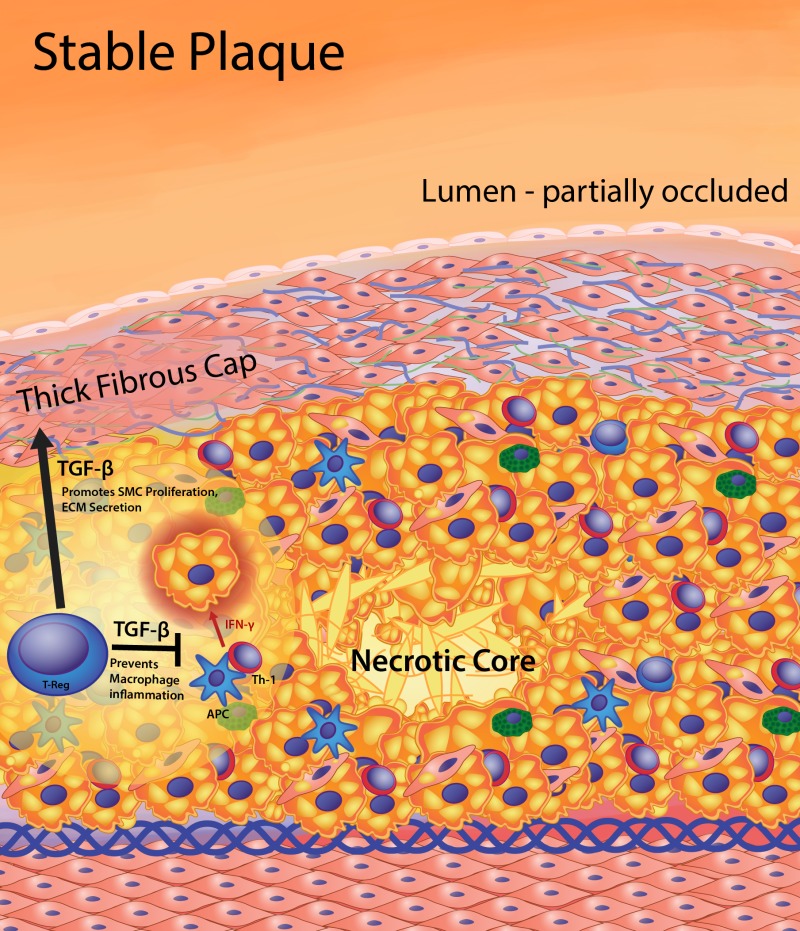
The Role Of Lipids And Lipoproteins In Atherosclerosis Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf
No comments for "Atherosclerosis Is Characterized by the Deposition of Lipids in the:"
Post a Comment